
Better-Than-Expected Canadian Jobs Report in July Shows Economy’s Resilience
The July Labour Force Survey, released this morning by Statistics Canada, reflects labour market conditions as of the week of July 12 to 18. Although public health restrictions had been substantially eased in most parts of the country—with the exception of some regions of Ontario, including Toronto—some measures remained in place, including physical distancing requirements and restrictions on large gatherings.
From February to April, 5.5 million Canadian workers–30% of the workforce–were affected by the COVID-19 economic shutdown. This included a drop in employment of 3.0 million and a COVID-related increase in absences from work of 2.5 million. Today’s jobs report showed that total employment rose by 418,500 (+2.4%). This is on the heels of a 953,000 (5.8%) gain in June and 290,000 in May. Altogether, this brought employment to within 1.3 million (-7.0%) of its pre-COVID February level.
The number of Canadians who were employed but worked less than half their usual hours for reasons likely virus-related dropped by 412,000 (-18.8%) in July. Combined with declines recorded in May and June, this left COVID-related absences from work at just under 1 million (+972,000; +120.3%) above February levels.
By the week of July 12 to July 18, the total number of affected workers stood at 2.3 million, a reduction since April of 58.0%.
MOST EMPLOYMENT GAINS IN JULY WERE IN PART-TIME WORK
Most of the employment gains in July were in part-time work, which increased by 345,000 (+11.3%), compared with a much smaller increase of 73,000 (+0.5%) in full-time work.
The COVID-19 labour market shock was felt particularly hard in part-time work. From February to April, losses in part-time work (-29.6%) were significantly heavier than in full-time employment (-12.5%). This was due to a number of factors, including part-time work being more prevalent in industries that were most affected by the COVID-19 economic shutdown, namely retail trade and accommodation and food services.
Growth in part-time employment has outpaced full-time growth in each of the past three months. With July gains, part-time work is now closer to its pre-COVID level (-5.0%) than full-time employment (-7.5%).
The relatively flat growth in full-time work in recent months is reflected in an increase in the proportion of part-time workers doing so involuntarily. In July 2019, 22.2% of those working less than 30 hours per week would have preferred full-time work. One year later, this proportion had increased 7.6 percentage points to 29.7%, an indication that the COVID-19 economic shutdown and subsequent re-opening has resulted in a reduction, at least temporarily, in the number of hours being offered by employers.
STRONGER EMPLOYMENT GAINS FOR WOMEN IN JULY, BUT MEN CONTINUE TO BE CLOSER TO PRE-SHUTDOWN LEVELS
In July, employment rose faster among women (+3.4% or +275,000) than men (+1.5% or +144,000). Due to heavier employment losses among women in March, however, employment in July was closer to its pre-shutdown level for men than for women.
Employment was little changed in July among both male and female core-aged workers with children under 18. As in June, employment in July was furthest away from pre-shutdown levels among mothers whose youngest child was aged 6 to 17.
THE NUMBER OF CANADIANS WORKING FROM HOME CONTINUED TO FALL IN JULY
Among those who were employed and not absent from work, the number working from home dropped by 400,000, compared with an increase of 300,000 in the number working at locations other than home. Despite this decline, the number of Canadians who worked from home in July (4.6 million) remained significantly higher than the number who usually do so (1.6 million).
THE PACE OF IMPROVEMENT FROM JULY ON IS LIKELY TO CONTINUE TO SLOW.
Compared to February, there were still 274,000 fewer people working in goods production jobs in July. There were still 309,000 fewer workers in accommodation and food services, 109,000 fewer in information, culture, and recreation, over that period – and those services jobs will probably be slower to return with households still sticking closer to home. The recovery in the goods-producing side of the economy will be limited at some point by ongoing weakness in the oil & gas sector.
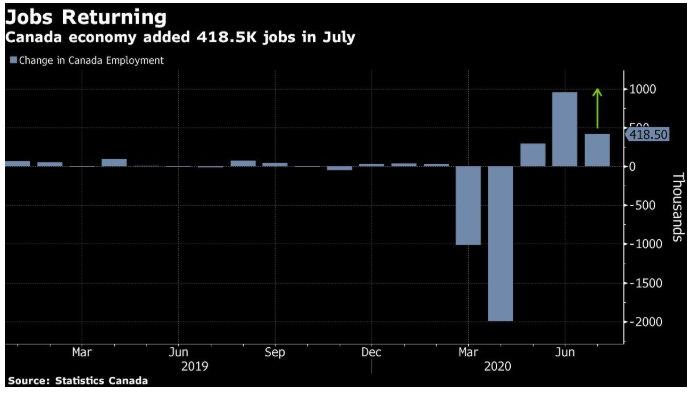
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE CONTINUES TO DROP FROM MAY’S RECORD HIGH
The unemployment rate was 10.9% in July, falling 1.4 percentage points for the second consecutive month and down from a record high of 13.7% in May. The unemployment rate was 5.6% in February.
The number of unemployed people fell for the second consecutive month in July, down 269,000 (-11.0%). Despite this decrease, almost 2.2 million Canadians were unemployed in July, nearly twice as many (+92.6%) as in February (1.1 million).
In July, temporary layoffs declined sharply for a second consecutive month, down 384,000 (-45.5%). Among those on temporary layoff in June, approximately half became employed in July, either returning to their old job or starting a new one (not seasonally adjusted). Despite the sharp declines in June and July, the number of people on temporary layoff (460,000) was more than four times higher than it was in February.
In July, the number of people searching for work increased 115,000 (+7.1%), mainly the result of people entering the labour force to look for work.
Employment Increases in Most Provinces in July–Led by Ontario and Quebec
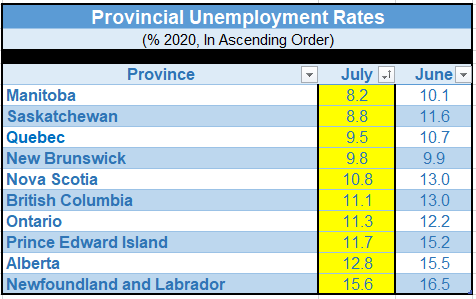
In Ontario, employment rose by 151,000 (+2.2%) in July, building on an increase of 378,000 in June and bringing jobs to 91.7% of its pre-pandemic February level. The initial easing of COVID-19 restrictions occurred later in Ontario than in most other provinces. Additional easing was introduced in most regions of the province on July 17, at the end of the survey week.
Employment in the census metropolitan area of Toronto increased by 2.2% in July. This was the same rate of increase as the province, despite the loosening of the COVID-19 restrictions occurring later in the provincial capital than in most other regions. Employment in Toronto reached 89.9% of its February level.
Employment in Quebec increased by 98,000 (+2.4%) in July, adding to gains in the previous two months and bringing employment to 94.4% of its pre-COVID level. The increase in employment in July was all in part-time work. The unemployment rate decreased 1.2 percentage points to 9.5%, the third consecutive monthly decrease.
Employment rose more slowly in Montréal (+28,000; +1.3%) than in the rest of Quebec and reached 94.4% of its February level.
The number of employed British Columbians increased by 70,000 (+3.0%) in July, reaching 93.5% of the February employment level. The unemployment rate fell by 1.9 percentage points to 11.1%.
In Vancouver, employment increased by 48,000 (+3.8%) to reach 89.9% of the February level, a degree of recovery lower than the province as a whole.
In Alberta, employment increased by 67,000 (+3.2%) in July, including gains in both full-time and part-time work. The unemployment rate for the province fell by 2.7 percentage points in July to 12.8%, the first decline since the COVID-19 economic shutdown.
In Saskatchewan, employment rose by 13,000 (+2.5%), while the unemployment rate fell 2.8 percentage points to 8.8%.
Employment in Manitoba increased (+12,000) for the third consecutive month, and the unemployment rate declined by 1.9 percentage points to 8.2%.
Employment in Newfoundland and Labrador increased by 4,300 (+2.1%) in July, and the unemployment rate dropped 0.9 percentage points to 15.6%.
In Nova Scotia, employment rose by 3,400 (+0.8%) in July, reaching 92.7% of its February level. The unemployment rate in the province declined by 2.2 percentage points to 10.8%.
Employment in Prince Edward Island rose by 1,100 in July (+1.5%), adding to the gains in the previous two months. The unemployment rate declined by 3.5 percentage points to 11.7%.
In New Brunswick, employment was little changed in July after recording employment gains of 39,000 from April to June. Employment in the province—which was among the first to begin easing COVID-19 restrictions—was at 96.6% of its pre-COVID February level, the most complete employment recovery of all provinces to date.
BOTTOM LINE
This was a strong jobs report, but the low-hanging fruit has already been picked. Undoubtedly, Canada’s economy is still digging itself out of a deep hole, and some jobs are gone for good. Accommodation and food services are still hard hit, as is leisure and entertainment.
Many small and some large businesses will not survive. But new sectors are proliferating as the pandemic accelerated the technological forces that were already in train. I expect to see strong job growth in the following new and burgeoning areas: telemedicine, big data, artificial intelligence, cloud services, cybersecurity, 5G, driverless transportation and clean energy. Online shopping will also continue to proliferate as Canadians have learned to use delivery services and online retail.
Unfortunately, those who can afford it least were hardest hit in the pandemic-shutdown. Many of the lost jobs will not return.
Canada has done an excellent job of flattening the pandemic curve, but as evidenced by what is happening in the US, we cannot let our guard down. As many students return to the classroom, the risk of disease spread will undoubtedly rise. Also, we have no idea what colder weather will bring or when a vaccine will be widely available. We must continue to prepare for the worst but hope for the best. In the meantime, our economy is proving its underlying resilience, and our government policies are cushioning the blow to those that are suffering the most.
South of the Border–US COVID Situation Is A Disaster
Nearly every country has struggled with the pandemic and made mistakes along the way. But the US stands alone among affluent countries in the failure of its pandemic response. In the past month, about 1.9 million Americans have tested positive for the virus. That’s more than five times as many as in all of Europe, Canada, Japan, South Korea and Australia, combined.
“Even though some of these countries saw worrying new outbreaks over the past month, including 50,000 new cases in Spain … the outbreaks still pale in comparison to those in the United States. Florida, with a population less than half of Spain, has reported nearly 300,000 cases in the same period,” wrote David Leonhardt of the New York Times yesterday.
Moreover, the end of July saw the expiration of the $600/week federal top-up of unemployment benefits, which to-date has been successful at providing a floor for household income, and subsequently helps boost household spending. As well, the prohibition of eviction has ended as Congress continues to wrangle on a new relief package.
Larry Kudlow, the administration’s chief economist, declared last week that a “V-shaped recovery” was still on track. There is no way that will be possible given the suspension or reduction in federal assistance, the rapidly depleting funds of the state and local governments who are, by law, not allowed to run budget deficits, and the continued surge in the disease.
Today’s July jobs report in the US showed the economic rebound was still making headway as payrolls increased by 1.76 million in July, beating economists estimates. The unemployment rate fell to 10.2%, while a broader gauge of joblessness also declined to 16.5%.
The path forward for the US will remain quite difficult as businesses use up the last of their federal loans and reduced unemployment benefits pressure consumer spending. The rebound in the US economy is fragile, as high-frequency data continue to indicate. For the week of July 31st, new COVID cases continue to worsen. Some states have had to halt or even backpedal reopening plans; same-store sales are falling, as are restaurant bookings, electricity demand, airline tickets and public transit ridership.
At the time of this writing, the latest headlines are screaming that “US Virus Aid Talks Are On the Brink of Collapse,” as Trump mulls over an executive order on some jobless aid. American consumer confidence can’t help but be badly battered by such incompetence, as the world looks on in utter disbelief.
Written by
Dr Sherry Cooper
Chief Economist, Dominion Lending Centres












